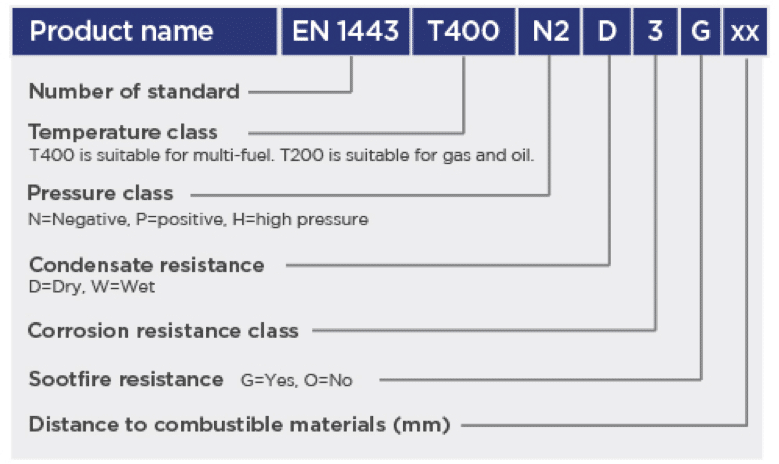
One of the key features of the European Standard for system metal chimneys is a user-readable classification system that designates the features of the product. A label showing the classification must go with each flue component. Understanding the classification can make the job of selecting the right flue much easier and will allow you to compare different flues. It’s easy to use so long as you know the keys. The diagrams below unlock the coded information.
EN 1443 – T400 N2 D 3 Gxx
The minimum designation required when burning wood in open or closed appliances and coal.
Temperature class – is the maximum flue operating temperature it has been approved for. (Many flexible liners will have a T600 classification.)
Pressure class – is the pressure it has been tested to N negative, P positive, H high pressure. The accompanying number is the amount of leakage at pressure tested at. Further information on this can be found in ADJ Table G2 pg. 78
Resistance to condensate class – is whether suitable for Dry or Wet application. Therefore, it will either be D or W
Corrosion resistance class – is what type of fuel it may be used for. 1,2,3, (see table below)
Sootfire resistance class – G means it has been tested to 1000 degrees C for 30 minutes within a test and the gas tightness was still met after the test. The xx is the distance to combustibles declared by the manufacturer when tested.
Please be aware that you can test a chimney without an enclosure and declare a Gxx distance which would give a different result if tested within an enclosure Gxx due to restricted ventilation when enclosed. The letter O means it has not been sootfire tested and thus is not suitable for use with solid fuel. It will show either G or O. (There would be no xx after the G on a flexible liner, as they are only permitted to be installed within a masonry flue.
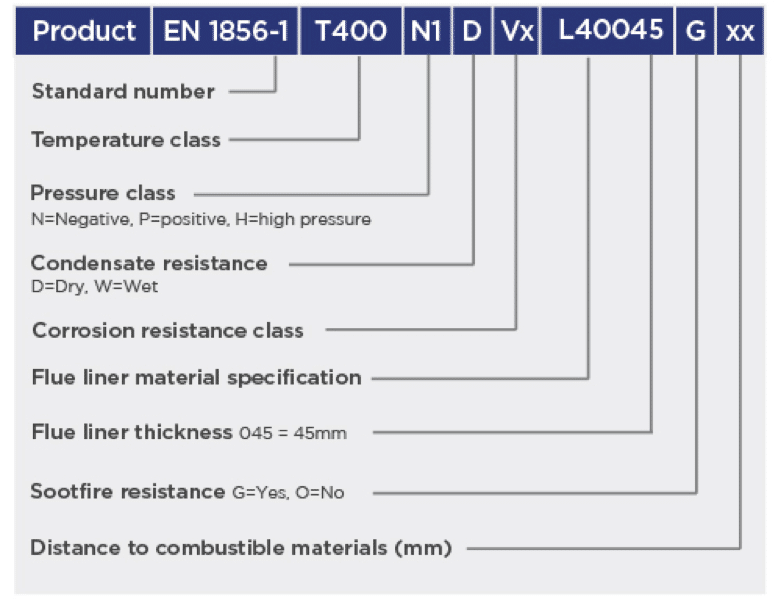
EN 1856-1:2009
Each type of chimney system has a test method, for a metal chimney it is BS EN1856-1:2009 so within this test we must meet the general requirements of EN 1443 using specified materials and test methods.
One of the key features of the European Standard for metal chimneys (EN 1856) is a user-readable classification system that designates the features of the product. A label showing the classification must go with each flue component. Understanding the classification can make the job of selecting the right flue much easier and will allow you to compare different flues.
Temperature Rating Maximum temperature (°C) for continuous use of the flue. T400 is suitable for multi-fuel. T200 is suitable for gas and oil.
Corrosion ResistanceThis is fuel dependent as follows;
V1 Resistant to attack from products of combustion from gas.
V2 Resistant to attack from products of combustion from light oil (sulphur content up to 0.2%) and natural wood. If the flue passes the V2 wet test then it is also deemed to comply with D3 & V3 under dry conditions.
D3 Resistant to the products of combustion from burning wood under dry conditions.
V3 Resistant to attack from products of combustion from heavy oil (sulphur content > 0.2%), solid fuels and peat.
VM Not tested but rating declared by the manufacturer.
Liner Material and Thickness 316L, is usually the highest quality grade used on system chimneys and is expected to withstand the corrosion effect of multi-fuel, wood or heavy oil. The code for 316L is L50. The only practical difference between 316 and 316L is carbon content. Light oil is less corrosive and normally 304 (L20) has proved adequate in dry conditions, but in the increasingly common wet conditions created by high efficiency condensing appliances, the higher grade is required (316L). Often many system chimneys will have a 316L inner skin and a 304 grade stainless steel outer skin, protected by the surrounding insulation. The thickness is the steel thickness in mm.
Soot Fire Resistance and Distance to Combustibles Expressed as either G, for soot fire resistance or O for not, followed by the declared minimum distance to combustibles expressed in mm. To obtain the G classification means that the product has been tested at 1000°C for 30 minutes and remains intact. The temperature of combustible material at the designated distance must not exceed 100°C at an ambient temperature of 20°C.
Distance to Combustibles for Connecting Flue Pipe Connecting flue pipes to BS EN 1856-2 also have an additional classification M (Measured) or NM (Not Measured). If not measured the minimum distance to combustibles should be 3 times the internal diameter of connecting flue pipe. Connecting flue pipes to BS EN 1856-1 should be used in accordance with the manufacture’s declared distance to combustibles.